Gibraltar | |
|---|---|
| Motto: | |
| Anthem: God Save the King | |
| Song: Gibraltar Anthem | |
 Location of Gibraltar (dark green) United Kingdom shown in pale green | |
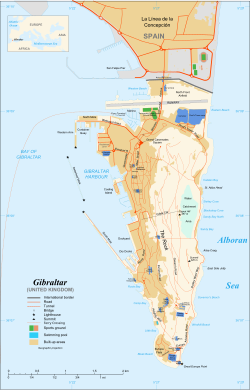 Map of Gibraltar | |
| Sovereign state | |
| Capture from Spain | 4 August 1704 |
| Cession to Great Britain | 11 April 1713 |
| National Day | 10 September 1967 |
| Accession to EEC | 1 January 1973 |
| Withdrawal from the EU | 31 January 2020 |
| Official languages | English |
| Spoken languages | |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Devolved representative dependency |
• Monarch | Charles III |
• Governor | Ben Bathurst |
| Fabian Picardo | |
• Mayor | Carmen Gómez[2] |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Government of the United Kingdom | |
• Minister | Stephen Doughty |
| Area | |
• Total | 6.8[3] km2 (2.6 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0 |
| Highest elevation | 426 m (1,398 ft) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 34,003[3] (220th) |
• 2022 census | 32,688 |
• Density | 5,000/km2 (12,949.9/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2013 estimate |
• Total | £1.64 billion (not ranked) |
• Per capita | £50,941 (not ranked) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | £2.911 billion[3] |
• Per capita | £85,614[3] |
| HDI (2018) | 0.961[4] very high · 3rd |
| Currency | Pound sterling Gibraltar pound (£) (GIP) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +350 |
| Postcode | GX11 1AA |
| Internet TLD | .gi |
| Website | www |


Gibraltar (/dʒɪˈbrɔːltər/ jib-RAWL-tər, Spanish: [xiβɾalˈtaɾ]) is a British Overseas Territory[a] and city[6] located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the Atlantic Ocean (Strait of Gibraltar).[7][8] It has an area of 6.8 km2 (2.6 sq mi)[3] and is bordered to the north by Spain (Campo de Gibraltar). The landscape is dominated by the Rock of Gibraltar, at the foot of which is a densely populated town area, home to some 34,003 people, primarily Gibraltarians.[9]
Gibraltar was founded as a permanent watchtower by the Almohads in 1160. It switched control between the Nasrids, Castilians and Marinids in the Late Middle Ages, acquiring larger strategic clout upon the destruction of nearby Algeciras c. 1375. It became again part of the Crown of Castile in 1462. In 1704, Anglo-Dutch forces captured Gibraltar from Spain during the War of the Spanish Succession, and it was ceded to Great Britain in perpetuity under the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713. It became an important base for the Royal Navy, particularly during the Napoleonic Wars and World War II, as it controlled the narrow entrance and exit to the Mediterranean Sea, the Strait of Gibraltar, with half the world's seaborne trade passing through it.[10][11][12]
The sovereignty of Gibraltar is a point of contention in Anglo-Spanish relations as Spain asserts a claim to the territory.[13][14] Gibraltarians overwhelmingly rejected proposals for Spanish sovereignty in a 1967 referendum, and for shared sovereignty in a 2002 referendum.[15][16] Nevertheless, Gibraltar maintains close economic and cultural links with Spain, with many Gibraltarians speaking Spanish as well as a local dialect known as Llanito.[17][18][19]
Gibraltar's economy rests on financial services, e-gaming, tourism and the port.[20] With one of the world's lowest unemployment rates, the largest part of the labour force are resident in Spain or non-Gibraltarians, especially in the private sector. Since Brexit, Gibraltar is not a member of the European Union but negotiations are under way to have it participate in the Schengen Agreement to facilitate border movements between Gibraltar and Spain.[21] As of March 2023[update], talks seem deadlocked.[22]
- ^ "National Symbols". Gibraltar.gov.gi. Archived from the original on 13 November 2014. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- ^ "Investiture of Ms Carmen Gomez GMD as Gibraltar's Mayor - 342/2023". 30 May 2023. Retrieved 12 June 2023.
- ^ a b c d e "Gibraltar - Key Indicators". Gibraltar.gov.gi. 2024. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ [1] Archived 9 August 2021 at the Wayback Machine Rankings – Human Development Index (HDI)
- ^ "Fourth Committee Hears Petitioners from Non-Self-Governing Territories, Including French Polynesia, New Caledonia, Gibraltar". United Nations. 2016. Archived from the original on 20 November 2021. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ^ "Better late than never: Gibraltar 'becomes' city after 180-year delay". The Guardian. 28 August 2022. Archived from the original on 28 August 2022. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ Dictionary.com: Gibraltar Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Free Dictionary: Gibraltar Archived 26 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Statistics Office (2009). "Abstract of Statistics 2009" (PDF). Statistics Office of the Government of Gibraltar. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 December 2014. Retrieved 12 November 2010. The civilian population includes Gibraltarian residents, other British residents (including the wives and families of UK-based servicemen, but not the servicemen themselves) and non-British residents. Visitors and transients are not included.
In 2009, this broke down into 23,907 native-born citizens, 3,129 UK British citizens and 2,395 others, making a total population of 29,431. On census night, there were 31,623 people present in Gibraltar. - ^ "Brexit makes Gibraltar even more important to the UK". British Foreign Policy Group. 24 November 2016. Archived from the original on 3 April 2017. Retrieved 2 April 2017.
- ^ "Gibraltar: what is at stake?". Telegraph. 21 July 2009. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 2 April 2017.
- ^ "Inside the rock: Gibraltar's strategic and military importance is complemented by financial and gaming leadership". City AM. 12 November 2015. Archived from the original on 3 April 2017. Retrieved 2 April 2017.
- ^ (in Spanish) Informe sobre la cuestión de Gibraltar, Spanish Foreign Ministry. Archived 25 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "History and Legal Aspects of the Dispute". The Ministry of Foreign Affairs, European Union and Cooperation. Archived from the original on 13 December 2018. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ Daly, Emma (8 November 2002). "Gibraltar Votes to Remain British". The Washington Post. Retrieved 28 January 2019.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hills-13was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ David Levey (January 2008). Language Change and Variation in Gibraltar. John Benjamins Publishing. pp. 1–4. ISBN 978-90-272-1862-9.
- ^ "Employment Survey 2022" (PDF). Government of Gibraltar. Retrieved 21 July 2023.
- ^ "Govt's stark analysis highlights Brexit border challenge". Gibraltar Chronicle. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- ^ Ravinesh Kumar, Ronald; Stauvermann, Peter Josef; Pate, Arvind (2015). "Nexus between electricity consumption and economic growth: a study of Gibraltar" (PDF). Economic Change and Restructuring. 48 (2). Springer: 120. doi:10.1007/s10644-014-9156-0. ISSN 1573-9414. S2CID 254472584.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
GibStatementwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
FT240323was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).

