This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (August 2007) |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2020) |
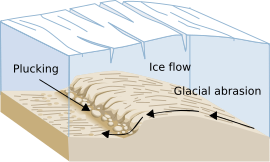
The glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had a profound effect on the surface features of the area over which it moved. Vast quantities of rock and soil were scraped from the glacial centers to its margins by slowly moving ice and redeposited as drift or till. Much of this drift was dumped into old preglacial river valleys, while some of it was heaped into belts of hills (terminal moraines) at the margin of the glacier. The chief result of glaciation has been the modification of the preglacial topography by the deposition of drift over the countryside. However, continental glaciers possess great power of erosion and may actually modify the preglacial land surface by scouring and abrading rather than by the deposition of the drift.
The marks of glaciation vastly altered Minnesota's topography. Probably the most significant change was in the character and extent of the drainage. In preglacial times, there is reason to believe that most of the rainwater or meltwater from snow was quickly carried back to the ocean. Today, much of the precipitation is retained temporarily on the surface in the lakes. Streams meander from lake to lake, and only part of the total precipitation is carried away by the rivers. Such topography could be described as immature because the streams have not yet been able to establish themselves into a network that quickly and efficiently drains the land. The Mississippi River has cut a deep valley below St. Anthony Falls, but even the waters of this large river do not flow freely to the ocean because of Lake Pepin, which acts as a storage basin for some of the water. Streams have been actively engaged in their erosive work only for the last 10,000 years, the estimated length of time since the last glacier began its final retreat. This time span is relatively insignificant compared to the long history of the Earth.