 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Copaxone,[1] Glatopa,[2] Brabio |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a603016 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Subcutaneous injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.248.824 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
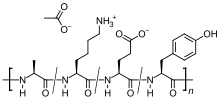
| Formula | C25H45N5O13 |
| Molar mass | 623.657 g·mol−1 |
| | |
Glatiramer acetate (also known as Copolymer 1, Cop-1), sold under the brand name Copaxone among others, is an immunomodulator medication used to treat multiple sclerosis.[1][2] Glatiramer acetate is approved in the United States to reduce the frequency of relapses, but not for reducing the progression of disability. Observational studies, but not randomized controlled trials, suggest that it may reduce progression of disability. While a conclusive diagnosis of multiple sclerosis requires a history of two or more episodes of symptoms and signs, glatiramer acetate is approved to treat a first episode anticipating a diagnosis. It is also used to treat relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection.[1][2]
It is a mixture of random-sized peptides that are composed of the four amino acids found in myelin basic protein, namely glutamic acid, lysine, alanine, and tyrosine. Myelin basic protein is the antigen in the myelin sheaths of the neurons that stimulates an autoimmune reaction in people with MS, so the peptide may work as a decoy for the attacking immune cells.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6]
- ^ a b c d "Copaxone- glatiramer acetate injection, solution". DailyMed. 23 July 2020. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Glatopa- glatiramer acetate injection, solution". DailyMed. 31 July 2020. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ "Neurological therapies". Health Canada. 9 May 2018. Retrieved 13 April 2024.
- ^ "Brabio 20 mg/mL Solution for Injection, Pre-filled Syringe - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ "Copaxone 20 mg/ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 29 September 2020. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.