Glycoalkaloids are a family of chemical compounds derived from alkaloids to which sugar groups are appended. Several are potentially toxic, most notably the poisons commonly found in the plant species Solanum dulcamara (bittersweet nightshade) and other plants in the genus Solanum, including potato.
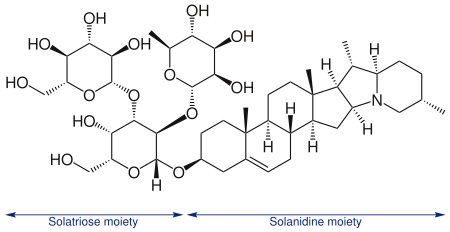
A prototypical glycoalkaloid is solanine (composed of the sugar solanose and the alkaloid solanidine), which is found in the potato. The alkaloidal portion of the glycoalkaloid is also generically referred to as an aglycone. The intact glycoalkaloid is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, therefore causing gastrointestinal irritation. The aglycone is absorbed and is believed to be responsible for observed nervous system signs.