| Great Bear Lake | |
|---|---|
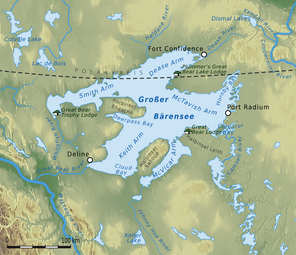 Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories | |
| Location | Northwest Territories |
| Coordinates | 65°50′01″N 120°45′06″W / 65.83361°N 120.75167°W[1] |
| Lake type | Glacial |
| Primary outflows | Great Bear River |
| Catchment area | 114,717 km2 (44,292 sq mi)[2][3] |
| Basin countries | Canada |
| Surface area | 31,153 km2 (12,028 sq mi)[2][3] |
| Average depth | 71.7 m (235 ft)[2][3] |
| Max. depth | 446 m (1,463 ft)[2][3] |
| Water volume | 2,234 km3 (536 cu mi)[2][3] |
| Residence time | 124 years[2] |
| Shore length1 | 2,719 km (1,690 mi) (plus 824 km (512 mi) island shoreline)[2][3] |
| Surface elevation | 156 m (512 ft) |
| Frozen | November - July[3] |
| Islands | 26 main islands, totalling 759.3 km2 (293.2 sq mi) in area[2] |
| Settlements | Délı̨nę |
| References | [2][3] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Great Bear Lake (Slave: Sahtú; French: Grand lac de l'Ours) is a lake in the boreal forest of Canada. It is the largest lake entirely in Canada (Lake Superior and Lake Huron are larger but straddle the Canada–US border), the fourth-largest in North America, and the eighth-largest in the world.[4] The lake is in the Northwest Territories, on the Arctic Circle between 65 and 67 degrees of northern latitude and between 118 and 123 degrees western longitude, 156 m (512 ft) above sea level.
The name originated from the Chipewyan word satudene, meaning "grizzly bear-water people". The Sahtu, a Dene people, are named after the lake. Grizzly Bear Mountain, or Sahoyue, on the shore of the lake also comes from Chipewyan, meaning "bear-large hill".[5][6]
Sahoyue (Grizzly Bear Mountain), a peninsula on the south side of the lake, and Edacho (Scented Grass Hills), another peninsula on the west side, form the Saoyú-ʔehdacho National Historic Site of Canada.[7][8]
- ^ "Great Bear Lake". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Johnson, L. (1975). "Physical and chemical characteristics of Great Bear Lake". J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 32 (11): 1971–1987. doi:10.1139/f75-234. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. (World Lakes Database)
- ^ a b c d e f g h Hebert, Paul (2007), "Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories", Encyclopedia of Earth, Washington, DC: Environmental Information Coalition, National Council for Science and the Environment, retrieved 7 December 2007
- ^ "World's largest lakes". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ^ Johnson, L. The Great Bear Lake: Its Place in History Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Calgary, Alberta: Arctic Institute of North America (AINA) database at the University of Calgary. pp. 236-237. Retrieved on: 30 January 2012.
- ^ "Natural Resources Canada-Canadian Geographical Names (Grizzly Bear Mountain)". Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ "Saoyú-ʔehdacho National Historic Site of Canada". Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ "Northwest Territories Protected Areas Strategy (Saoyú-ʔehdacho)". Archived from the original on 11 August 2016. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
