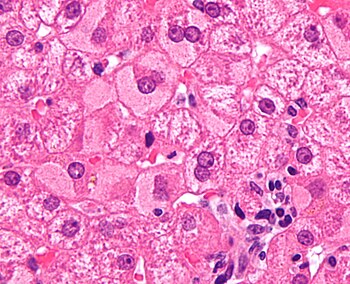
In liver pathology, a ground glass hepatocyte, abbreviated GGH, is a liver parenchymal cell with a flat hazy and uniformly dull appearing cytoplasm on light microscopy. The cytoplasm's granular homogeneous eosinophilic staining is caused by the presence of HBsAg.
The appearance is classically associated with abundant hepatitis B antigen in the endoplasmic reticulum, but may also be drug-induced.[1][2] In the context of hepatitis B, GGHs are only seen in chronic infections, i.e. they are not seen in acute hepatitis B.
GGHs were first described by Hadziyannis et al.[2][3]
- ^ Cohen, C (Aug 1975). ""Ground-glass" hepatocytes". S Afr Med J. 49 (34): 1401–3. PMID 1162516.
- ^ a b Su, IJ; Wang, HC; Wu, HC; Huang, WY (Aug 2008). "Ground glass hepatocytes contain pre-S mutants and represent preneoplastic lesions in chronic hepatitis B virus infection". J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23 (8 Pt 1): 1169–74. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05348.x. PMID 18505413.
- ^ Hadziyannis, S; Gerber, MA; Vissoulis, C; Popper, H (Nov 1973). "Cytoplasmic hepatitis B antigen in "ground-glass" hepatocytes of carriers". Arch Pathol. 96 (5): 327–30. PMID 4582440.