Guadeloupe
Gwadloup (Guadeloupean Creole French) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: La Marseillaise ("The Marseillaise") | |
 Location in the Lesser Antilles | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 16°15′N 61°30′W / 16.250°N 61.500°W | |
| Country | |
| Prefecture | Basse-Terre |
| Largest metropolitan area | Pointe-à-Pitre |
| French colony | 1648 |
| English occupation | 1759 |
| Restitution to France | 10 February 1763 |
| Second English occupation | 1782 |
| Second restitution to France | 30 May 1814 a |
| Communes | 32 |
| Government | |
| • President of the Departmental Council | Guy Losbar[1] |
| • President of the Regional Council | Ary Chalus |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,628 km2 (629 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 16th region |
| Highest elevation | 1,467 m (4,813 ft) |
| Population (1 January 2024)[2] | |
• Total | 378,561 |
| • Density | 230/km2 (600/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Guadeloupean |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €9.462 billion |
| • Per capita | €22,500 |
| Time zone | UTC-4:00 (AST) |
| Area code | +590 |
| ISO 3166 code | |
| Internet TLD | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Languages | |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Website | www www |
| a Not effective until 1816. | |
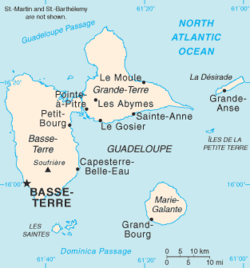
Guadeloupe (/ˌɡwɑːdəˈluːp/; French: [ɡwad(ə)lup] ; Guadeloupean Creole French: Gwadloup, IPA: [ɡwadlup]) is an overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean.[4] It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and two Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings.[5] It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat and north of Dominica. The capital city is Basse-Terre, on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both on Grande-Terre Island.[4] It had a population of 395,726 in 2024.[2]
Like the other overseas departments, it is an integral part of France. As a constituent territory of the European Union and the Eurozone, the euro is its official currency and any European Union citizen is free to settle and work there indefinitely, but is not part of the Schengen Area. It included Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin until 2007, when they were detached from Guadeloupe following a 2003 referendum.
Christopher Columbus visited Guadeloupe in 1493 and gave the island its name. The official language is French; Antillean Creole is also spoken.[4][5]
- ^ "Répertoire national des élus: les conseillers départementaux". data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises (in French). 4 May 2022. Archived from the original on 13 December 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- ^ a b "Estimation de population par région, sexe et grande classe d'âge – Années 1975 à 2024" (in French). Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ "EU regions by GDP, Eurostat". Archived from the original on 27 February 2023. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ a b c "Encyclopedia Britannica – Guadeloupe". Archived from the original on 3 April 2019. Retrieved 27 July 2019.
- ^ a b "CIA World Factbook (2006) – Guadeloupe". Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 27 July 2019.

