| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
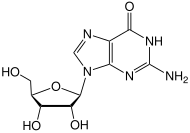
| IUPAC name
Guanosine[1]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-Amino-9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one | |
| Other names
Guanine riboside
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.844 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Guanosine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13N5O5 | |
| Molar mass | 283.241 |
| Appearance | white, crystalline powder[2] |
| Odor | odorless[2] |
| Melting point | 239 (decomposes)[3] |
| -149.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine.
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 1421. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b Robert A. Lewis, Michael D. Larrañaga, Richard J. Lewis Sr. (2016). Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary (16th ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 688. ISBN 978-1-118-13515-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ William M. Haynes (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. pp. 3–286. ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3.