| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
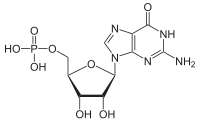
| IUPAC name
5′-Guanylic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-Amino-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | GMP |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.453 |
| E number | E626 (flavour enhancer) |
| MeSH | Guanosine+monophosphate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N5O8P | |
| Molar mass | 363.223 g·mol−1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.7, 2.4, 6.1, 9.4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), also known as 5′-guanidylic acid or guanylic acid (conjugate base guanylate), is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine; hence it is a ribonucleotide monophosphate. Guanosine monophosphate is commercially produced by microbial fermentation.[1]
As an acyl substituent, it takes the form of the prefix guanylyl-.
- ^ "The Vegetarian Resource Group Blog". www.vrg.org. Retrieved 25 April 2018.