| HLA-A69 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MHC Class I, A cell surface antigen) | ||||||||||||||||
 HLA-A69 | ||||||||||||||||
| About | ||||||||||||||||
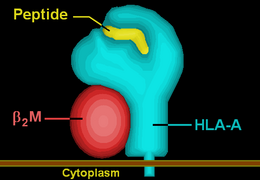
| Protein | transmembrane receptor/ligand | |||||||||||||||
| Structure | αβ heterodimer | |||||||||||||||
| Subunits | HLA-A*69--, β2-microglobulin | |||||||||||||||
| Older names | A28 | |||||||||||||||
| Subtypes | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Alleles link-out to IMGT/HLA database at EBI | ||||||||||||||||
HLA-A69 (A69) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α69 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A69, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*69 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus.[1] This group currently is dominated by A*6901. A69 and A*69 are almost synonymous in meaning. A69 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A28. A69 is a sister serotype of A68.
A69 is more common in Levant. A69 (A*6901) is a derivative of the A*6801 allele that has undergone gene conversion with A*02. The recombination took place no more than 330,000 years ago[2].
Serotype
[edit]| A*69 | A69 | A28 | A68 | A2 | Sample |
| allele | % | % | % | % | size (N) |
| *6901 | 7 | 56 | 3 | 6 | 289 |
A69 is poor, with low specific detection, high non-specific identification by A28, and false recognition by A68 and A2.
- ^ Arce-Gomez B, Jones EA, Barnstable CJ, Solomon E, Bodmer WF (February 1978). "The genetic control of HLA-A and B antigens in somatic cell hybrids: requirement for beta2 microglobulin". Tissue Antigens. 11 (2): 96–112. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01233.x. PMID 77067.
- ^ Holmes N, Parham P (1985). "Exon shuffling in vivo can generate novel HLA class I molecules". EMBO J. 4 (11): 2849–2854. PMC 554588. PMID 3877632.
- ^ Allele Query Form IMGT/HLA - European Bioinformatics Institute