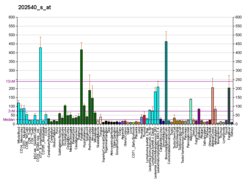
| hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADH) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.1.1.88 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 37250-24-1 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
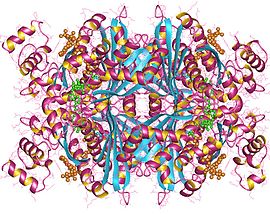 HMG-CoA reductase (NADPH), Human | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.1.1.34 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-controlling enzyme (NADH-dependent, EC 1.1.1.88; NADPH-dependent, EC 1.1.1.34) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia.
HMG-CoA reductase is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, and was long regarded as having seven transmembrane domains, with the active site located in a long carboxyl terminal domain in the cytosol. More recent evidence shows it to contain eight transmembrane domains.[5]
In humans, the gene for HMG-CoA reductase (NADPH) is located on the long arm of the fifth chromosome (5q13.3-14).[6] Related enzymes having the same function are also present in other animals, plants and bacteria.
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000113161 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021670 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Roitelman J, Olender EH, Bar-Nun S, Dunn WA, Simoni RD (June 1992). "Immunological evidence for eight spans in the membrane domain of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: implications for enzyme degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum". The Journal of Cell Biology. 117 (5): 959–973. doi:10.1083/jcb.117.5.959. PMC 2289486. PMID 1374417.
- ^ Lindgren V, Luskey KL, Russell DW, Francke U (December 1985). "Human genes involved in cholesterol metabolism: chromosomal mapping of the loci for the low density lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase with cDNA probes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (24): 8567–8571. Bibcode:1985PNAS...82.8567L. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.24.8567. PMC 390958. PMID 3866240.