| Hammick reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Dalziel Hammick |
| Reaction type | Coupling reaction |
The Hammick reaction, named after Dalziel Hammick, is a chemical reaction in which the thermal decarboxylation of α-picolinic (or related) acids in the presence of carbonyl compounds forms 2-pyridyl-carbinols.[1][2][3]
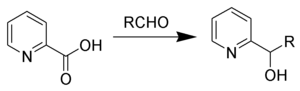
Using p-cymene as solvent has been shown to increase yields.[4]
- ^ Dyson, P.; Hammick, D. L. (1937). "362. Experiments on the mechanism of decarboxylation. Part I. Decomposition of quinaldinic and isoquinaldinic acids in the presence of compounds containing carbonyl groups". J. Chem. Soc.: 1724. doi:10.1039/jr9370001724.
- ^ Hammick, D. L.; Dyson, P. (1939). "172. The mechanism of decarboxylation. Part II. The production of cyanide-like ions from α-picolinic, quinaldinic, and isoquinaldinic acids". J. Chem. Soc.: 809–812. doi:10.1039/jr9390000809.
- ^ Brown, E. V.; Shambhu, M. B. (1971). "Hammick reaction of methoxypyridine-2-carboxylic acids with benzaldehyde. Preparation of methoxy-2-pyridyl phenyl ketones". J. Org. Chem. 36 (14): 2002. doi:10.1021/jo00813a034.
- ^ Sperber, N.; Papa, D.; Schwenk, E.; Sherlock, M. (1949). "Pyridyl-Substituted Alkamine Ethers as Antihistaminic Agents". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 71 (3): 887–90. doi:10.1021/ja01171a034. PMID 18113525.