| Haplogroup R1b | |
|---|---|
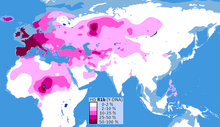 | |
| Possible time of origin | Probably soon after R1, possibly between 18,000-14,000 BC[1] |
| Possible place of origin | Western Asia, North Eurasia or Eastern Europe[2] |
| Ancestor | R1 |
| Descendants |
|
| Defining mutations | M343 |
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and across the Sahel in Central Africa, namely: Cameroon, Chad, Guinea, Mauritania, Mali, Niger, Nigeria and Senegal (concentrated in parts of Chad with concentration in the Hausa Tribe and among the Chadic-speaking ethnic groups of Cameroon).
The clade is also present at lower frequencies throughout Eastern Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia as well as parts of North Africa, South Asia and Central Asia.
R1b has two primary branches: R1b1-L754 and R1b2-PH155. R1b1-L754 has two major subclades: R1b1a1b-M269, which predominates in Western Europe, and R1b1b-V88, which is today common in parts of Central Africa. The other branch, R1b2-PH155, is so rare and widely dispersed that it is difficult to draw any conclusions about its origins. It has been found in Bahrain, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Ladakh, Tajikistan, Turkey, and Western China.
According to ancient DNA studies, most R1a and R1b lineages would have expanded from the Pontic Steppe along with the Indo-European languages.[2][3][4][5][6]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
fu2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Haak et al. 2015.
- ^ Allentoft ME, Sikora M, Sjögren KG, Rasmussen S, Rasmussen M, Stenderup J, et al. (June 2015). "Population genomics of Bronze Age Eurasia". Nature. 522 (7555): 167–72. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..167A. doi:10.1038/nature14507. PMID 26062507. S2CID 4399103.
- ^ Mathieson I, Lazaridis I, Rohland N, Mallick S, Patterson N, Roodenberg SA, et al. (2015). "Eight thousand years of natural selection in Europe". bioRxiv: 016477. doi:10.1101/016477. S2CID 7866359.
- ^ Cassidy LM, Martiniano R, Murphy EM, Teasdale MD, Mallory J, Hartwell B, Bradley DG (January 2016). "Neolithic and Bronze Age migration to Ireland and establishment of the insular Atlantic genome". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (2): 368–73. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113..368C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1518445113. PMC 4720318. PMID 26712024.
- ^ Martiniano R, Cassidy LM, Ó'Maoldúin R, McLaughlin R, Silva NM, Manco L, et al. (July 2017). "The population genomics of archaeological transition in west Iberia: Investigation of ancient substructure using imputation and haplotype-based methods". PLOS Genetics. 13 (7): e1006852. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1006852. PMC 5531429. PMID 28749934.