Harvey C. Nathanson (October 22, 1936 – November 22, 2019) was an American electrical engineer who, with engineer Robert A. Wickstrom, invented the first MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical systems) device of the type now found in products ranging from iPhones to automobiles.
MEMS devices, which are made using integrated circuit fabrication techniques, are composed of small moving mechanical elements that generally range from 1 to 100 micrometres (0.001 to 0.1 mm) in size. Typical MEMS devices include the accelerometers found in smartphones and video game controllers, and the gyroscopes used in automobiles and wearables.
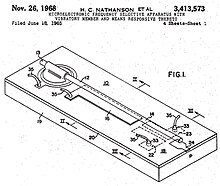
Nathanson and Wickstrom conceived the first MEMS device in 1965 to serve as a tuner for microelectronic radios.[1] It was developed also with William E. Newell at Westinghouse Research Labs in Pittsburgh, PA., and patented as a Microelectric Frequency Selective Apparatus.[2]
A refined version of the device was subsequently patented as the Resonant Gate Transistor.[3]
In their work developing similar devices, Nathanson, Wickstrom and team pioneered a method of batch fabrication in which layers of insulators and metal on silicon wafers are shaped and undercut through the use of masks and sacrificial layers, a process that would later become a mainstay of MEMS manufacturing.[4]
In 1973 he patented the use of millions of microscopically small moving mirrors to create a video display of the type now found in digital projectors.[5]
In 2000 Nathanson was awarded the Millennium Medal by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers for "outstanding contributions to the Society and to the field of electron devices."[6]
A graduate of Carnegie Mellon University, he holds more than 50 patents in the field of solid-state electronics.[7]
- ^ "A Resonant-Gate Silicon Surface Transistor with High-Q Band-Pass Properties". Applied Physics Letters. 15 August 1965. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
- ^ US patent 3413573, Nathanson et al, "Microelectronic frequency selective apparatus with vibratory member and means responsive thereto", issued 1968-11-26
- ^ US patent 3590343, Nathanson et al, "Resonant gate transistor with fixed position electronically floating gate electrode in addition to resonant member", issued 1971-6-29
- ^ "MicroElectroMechanical Systems (MEMS)". ProQuest. October 2001. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
- ^ US patent 3746911, Nathanson et al, "Electrostatically deflectable light valves for projection displays", issued 1973-7-17
- ^ "IEEE EDS Millennium Medal Winners". IEEE Electron Devices Society. 5 August 2010. Archived from the original on 13 September 2015. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
- ^ "Harvey C. Nathanson patents". Google Patents. Retrieved 14 August 2020.