Parts of this article (those related to Electronic health records) need to be updated. The reason given is: talks about 2020 as a future date. (March 2022) |
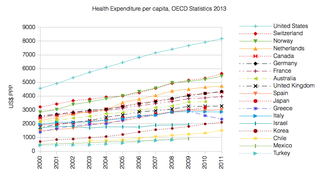

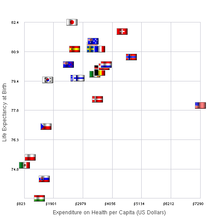

Switzerland has universal health care,[3] regulated by the Swiss Federal Law on Health Insurance. There are no free state-provided health services, but private health insurance is compulsory for all persons residing in Switzerland (within three months of taking up residence or being born in the country).[4][5][6]
Health insurance covers the costs of medical treatment and hospitalisation of the insured. However, the insured person pays part of the cost of treatment. This is done (a) by means of an annual deductible (called the franchise), which ranges from CHF 300 (PPP-adjusted US$ 489) to a maximum of CHF 2,500 (PPP-adjusted $4,076) for an adult as chosen by the insured person (premiums are adjusted accordingly) and (b) by a charge of 10% of the costs over and above the excess up to a stop-loss amount of CHF 700 (PPP-adjusted $1,141).
- ^ "OECD.StatExtracts, Health, Health Expenditure and Financing, Main Indicators, Health Expenditure since 2000" (Online Statistics). OECD.Stats. OECD's iLibrary. 2013. Retrieved 27 November 2013.
- ^ "OECD.StatExtracts, Health, Health Status, Life expectancy, Total population at birth, 2011" (Online Statistics). OECD.Stats. OECD's iLibrary. 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- ^ Schwartz, Nelson D. (1 October 2009). "Swiss health care thrives without public option". The New York Times. p. A1.
- ^ "Requirement to take out insurance, "Frequently Asked Questions" (FAQ)". Swiss Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH), Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA. 8 January 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 21 November 2013.
- ^ "Requirement to take out insurance: Persons residing in Switzerland". Swiss Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH), Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA. 8 January 2012. Retrieved 21 November 2013.
- ^ "The compulsory health insurance in Switzerland: Your questions, our answers". Swiss Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH), Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA. 21 December 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 21 November 2013.