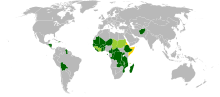
The heavily indebted poor countries (HIPC) are a group of 39 developing countries with high levels of poverty and debt overhang. Because of these factors, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank have classified them as eligible for special assistance.
The HIPC Initiative was initiated by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank in 1996, following extensive lobbying by NGOs and other bodies. It provides debt relief and low-interest loans to cancel or reduce external debt repayments to sustainable levels. This means the nations can repay debts in a timely fashion in the future.[1] To be considered for the initiative, countries must face an unsustainable debt burden that cannot be managed with traditional means.[2] Assistance is conditional on the national governments of these countries meeting a range of economic management and performance targets and undertaking economic and social reforms.[1][3]
- ^ a b "Developing Countries: Status Of The Heavily Indebted Poor Countries Debt Relief Initiative: NSIAD-98-229." GAO Reports (1998): 1. MasterFILE Premier. Web. 10 Sept. 2015.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
imffactsheetwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
wbwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).