| Hepatitis | |
|---|---|
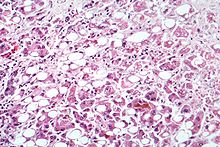 | |
| Alcoholic hepatitis as seen with a microscope, showing fatty changes (white circles), remnants of dead liver cells, and Mallory bodies (twisted-rope shaped inclusions within some liver cells). (H&E stain) | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease, gastroenterology, hepatology |
| Symptoms | Yellowish skin, poor appetite, abdominal pain[1][2] |
| Complications | Scarring of the liver, liver failure, liver cancer[3] |
| Duration | Short term or long term[1] |
| Causes | Viruses, alcohol, toxins, autoimmune[2][3] |
| Prevention | Vaccination (for viral hepatitis),[2] avoiding excessive alcohol |
| Treatment | Medication, liver transplant[1][4] |
| Frequency | > 500 million cases[3] |
| Deaths | > One million a year[3] |
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue.[3][5] Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.[1][2] Hepatitis is acute if it resolves within six months, and chronic if it lasts longer than six months.[1][6] Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure.[7] Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer.[3][8]
Hepatitis is most commonly caused by the virus hepatovirus A, B, C, D, and E.[2][3] Other viruses can also cause liver inflammation, including cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and yellow fever virus. Other common causes of hepatitis include heavy alcohol use, certain medications, toxins, other infections, autoimmune diseases,[2][3] and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).[9] Hepatitis A and E are mainly spread by contaminated food and water.[3] Hepatitis B is mainly sexually transmitted, but may also be passed from mother to baby during pregnancy or childbirth and spread through infected blood.[3] Hepatitis C is commonly spread through infected blood such as may occur during needle sharing by intravenous drug users.[3] Hepatitis D can only infect people already infected with hepatitis B.[3]
Hepatitis A, B, and D are preventable with immunization.[2] Medications may be used to treat chronic viral hepatitis.[1] Antiviral medications are recommended in all with chronic hepatitis C, except those with conditions that limit their life expectancy.[10] There is no specific treatment for NASH; physical activity, a healthy diet, and weight loss are recommended.[9] Autoimmune hepatitis may be treated with medications to suppress the immune system.[11] A liver transplant may be an option in both acute and chronic liver failure.[4]
Worldwide in 2015, hepatitis A occurred in about 114 million people, chronic hepatitis B affected about 343 million people and chronic hepatitis C about 142 million people.[12] In the United States, NASH affects about 11 million people and alcoholic hepatitis affects about 5 million people.[9][13] Hepatitis results in more than a million deaths a year, most of which occur indirectly from liver scarring or liver cancer.[3][14] In the United States, hepatitis A is estimated to occur in about 2,500 people a year and results in about 75 deaths.[15] The word is derived from the Greek hêpar (ἧπαρ), meaning "liver", and -itis (-ῖτις), meaning "inflammation".[16]
- ^ a b c d e f "Hepatitis". MedlinePlus. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g "What is hepatitis?". WHO. July 2016. Archived from the original on 7 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Hepatitis". NIAID. Archived from the original on 4 November 2016. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- ^ a b "Liver Transplant". NIDDK. April 2012. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ "Hepatitis". MedlinePlus. 2020-05-20. Retrieved 2020-07-19.
Your liver is the largest organ inside your body. It helps your body digest food, store energy, and remove poisons. Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver.
- ^ "Hepatitis (Hepatitis A, B, and C) | ACG Patients". patients.gi.org. Archived from the original on 2017-02-23.
- ^ Bernal W.; Wendon J. (2013). "Acute Liver Failure". New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (26): 2525–2534. doi:10.1056/nejmra1208937. PMID 24369077. S2CID 205116503.
- ^ "Esto es la hepatitis: Conócela, enfréntate a ella". Infoterio Noticias | Ciencia y Tecnología (in Spanish). 8 August 2022. Retrieved 2023-02-12.
- ^ a b c "Fatty Liver Disease (Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis)". NIDDK. May 2014. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ AASLD/IDSA HCV Guidance Panel (2015-09-01). "Hepatitis C guidance: AASLD-IDSA recommendations for testing, managing, and treating adults infected with hepatitis C virus". Hepatology. 62 (3): 932–954. doi:10.1002/hep.27950. ISSN 1527-3350. PMID 26111063.
- ^ "Autoimmune Hepatitis". NIDDK. March 2014. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ Vos, Theo; Allen, Christine; Arora, Megha; Barber, Ryan M.; Bhutta, Zulfiqar A.; Brown, Alexandria; Carter, Austin; Casey, Daniel C.; Charlson, Fiona J.; Chen, Alan Z.; Coggeshall, Megan; Cornaby, Leslie; Dandona, Lalit; Dicker, Daniel J.; Dilegge, Tina; Erskine, Holly E.; Ferrari, Alize J.; Fitzmaurice, Christina; Fleming, Tom; Forouzanfar, Mohammad H.; Fullman, Nancy; Gething, Peter W.; Goldberg, Ellen M.; Graetz, Nicholas; Haagsma, Juanita A.; Hay, Simon I.; Johnson, Catherine O.; Kassebaum, Nicholas J.; Kawashima, Toana; et al. (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". The Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ^ Basra, Sarpreet (2011). "Definition, epidemiology and magnitude of alcoholic hepatitis". World Journal of Hepatology. 3 (5): 108–13. doi:10.4254/wjh.v3.i5.108. PMC 3124876. PMID 21731902.
- ^ Wang, Haidong; Naghavi, Mohsen; Allen, Christine; Barber, Ryan M.; Bhutta, Zulfiqar A.; Carter, Austin; Casey, Daniel C.; Charlson, Fiona J.; Chen, Alan Zian; Coates, Matthew M.; Coggeshall, Megan; Dandona, Lalit; Dicker, Daniel J.; Erskine, Holly E.; Ferrari, Alize J.; Fitzmaurice, Christina; Foreman, Kyle; Forouzanfar, Mohammad H.; Fraser, Maya S.; Fullman, Nancy; Gething, Peter W.; Goldberg, Ellen M.; Graetz, Nicholas; Haagsma, Juanita A.; Hay, Simon I.; Huynh, Chantal; Johnson, Catherine O.; Kassebaum, Nicholas J.; Kinfu, Yohannes; et al. (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". The Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- ^ "Statistics & Surveillance Division of Viral Hepatitis CDC". CDC. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ "Online Etymology Dictionary". Etymonline.com. Archived from the original on 2012-10-20. Retrieved 2012-08-26.