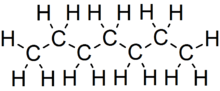
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Heptane[2] | |
| Other names
Septane[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1730763 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 49760 | |
| MeSH | n-heptane |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1206 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H16 | |
| Molar mass | 100.205 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Petrolic |
| Density | 0.6795 g cm−3[3] |
| Melting point | −90.549[3] °C (−130.988 °F; 182.601 K) |
| Boiling point | 98.38[3] °C (209.08 °F; 371.53 K) |
| 0.0003% (20 °C)[4] | |
| log P | 4.274 |
| Vapor pressure | 5.33 kPa (at 20.0 °C) |
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
12 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| −85.24·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3855[3] |
| Viscosity | 0.389 mPa·s[5] |
| 0.0 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
224.64 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
328.57 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−225.2 – −223.6 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−4.825 – −4.809 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H225, H304, H315, H336, H410 | |
| P210, P261, P273, P301+P310, P331 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −4.0 °C (24.8 °F; 269.1 K) |
| 223.0 °C (433.4 °F; 496.1 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.05–6.7% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
17,986 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)[6] |
LCLo (lowest published)
|
16,000 ppm (human) 15,000 ppm (mouse, 30 min)[6] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 500 ppm (2000 mg/m3)[4] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 85 ppm (350 mg/m3) C 440 ppm (1800 mg/m3) [15-minute][4] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
750 ppm[4] |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanes
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Heptane or n-heptane is the straight-chain alkane with the chemical formula H3C(CH2)5CH3 or C7H16. When used as a test fuel component in anti-knock test engines, a 100% heptane fuel is the zero point of the octane rating scale (the 100 point is 100% iso-octane). Octane number equates to the anti-knock qualities of a comparison mixture of heptane and iso-octane which is expressed as the percentage of iso-octane in heptane, and is listed on pumps for gasoline (petrol) dispensed globally.
- ^ Hofmann, August Wilhelm Von (1 January 1867). "I. On the action of trichloride of phosphorus on the salts of the aromatic monamines". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 15: 54–62. doi:10.1098/rspl.1866.0018. S2CID 98496840.
- ^ "n-heptane – Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
- ^ a b c d Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 3.290. ISBN 1-4398-5511-0.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0312". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Dymond, J. H.; Oye, H. A. (1994). "Viscosity of Selected Liquid n-Alkanes". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. 23 (1): 41–53. Bibcode:1994JPCRD..23...41D. doi:10.1063/1.555943. ISSN 0047-2689.
- ^ a b "n-Heptane". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
