| Hereditary coproporphyria | |
|---|---|
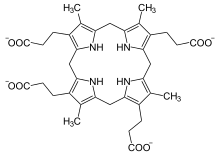 | |
| Coproporphyrinogen III | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria.[1] HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the CPOX gene, and is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, although homozygous individuals have been identified. Unlike acute intermittent porphyria, individuals with HCP can present with cutaneous findings similar to those found in porphyria cutanea tarda in addition to the acute attacks of abdominal pain, vomiting and neurological dysfunction characteristic of acute porphyrias. Like other porphyrias, attacks of HCP can be induced by certain drugs, environmental stressors or diet changes. Biochemical and molecular testing can be used to narrow down the diagnosis of a porphyria and identify the specific genetic defect. Overall, porphyrias are rare diseases. The combined incidence for all forms of the disease has been estimated at 1:20,000. The exact incidence of HCP is difficult to determine, due to its reduced penetrance.
- ^ "#121300 COPROPORPHYRIA, HEREDITARY; HCP". Johns Hopkins University. Retrieved 2012-05-27.