| Hereditary stomatocytosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Stomatocytes | |
| Specialty | Hematology |
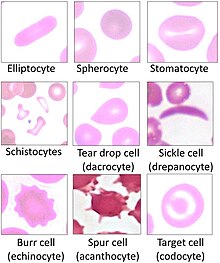
Hereditary stomatocytosis describes a number of inherited, mostly autosomal dominant human conditions which affect the red blood cell and create the appearance of a slit-like area of central pallor (stomatocyte) among erythrocytes on peripheral blood smear. The erythrocytes' cell membranes may abnormally 'leak' sodium and/or potassium ions, causing abnormalities in cell volume.[1] Hereditary stomatocytosis should be distinguished from acquired causes of stomatocytosis, including dilantin toxicity and alcoholism, as well as artifact from the process of preparing peripheral blood smears.[2]: 237
- ^ Andolfo I, Russo R, Gambale A, Iolascon A (January 2018). "Hereditary stomatocytosis: An underdiagnosed condition". American Journal of Hematology. 93 (1): 107–121. doi:10.1002/ajh.24929. PMID 28971506.
- ^ Tyrrell, L; Rose, G; Shukri, A; Kawash, SB (2021). "Morphologic changes in red blood cells: An illustrated review of clinically important light microscopic findings" (PDF). The Malaysian Journal of Pathology. 43 (2): 219–239. PMID 34448787. Retrieved 12 September 2022.