| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2,4,4,6,6-Hexafluoro-1,3,5,2λ5,4λ5,6λ5-triazatriphosphinine
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.019 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
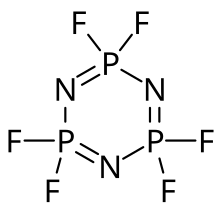
| (NPF2)3 | |
| Molar mass | 248.933 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder or lumps[1] |
| Melting point | 27 °C (81 °F; 300 K) |
| Boiling point | 51 °C (124 °F; 324 K) |
| decomposes | |
| Solubility | Toluene[1] |
| Structure | |
| Planar P3N3 ring | |
| 0 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P310, P305+P351+P338+P310, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hexafluorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the formula (NPF2)3. It takes the form of a white powder or lumps. It is sensitive to moisture and heat.[1]
- ^ a b c "Hexafluorocyclotriphosphazene 15599-91-4 | TCI AMERICA". www.tcichemicals.com.