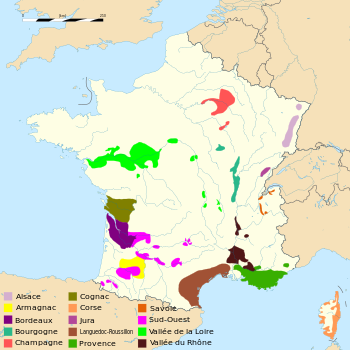
The history of French wine, spans a period of at least 2600 years dating to the founding of Massalia in the 6th century BC by Phocaeans with the possibility that viticulture existed much earlier. The Romans did much to spread viticulture across the land they knew as Gaul, encouraging the planting of vines in areas that would become the well known wine regions of Bordeaux, Burgundy, Alsace, Champagne, Languedoc, Loire Valley and the Rhone.
Over the course of its history, the French wine industry would be influenced and driven by the commercial interests of the lucrative English market and Dutch traders. Prior to the French Revolution, the Catholic Church was one of France's largest vineyard owners-wielding considerable influence in regions such as Champagne and Burgundy where the concept of terroir first took root. Aided by these external and internal influences, the French wine industry has been the pole bearer for the world wine industry for most of its history with many of its wines considered the benchmark for their particular style. The late 20th and early 21st century brought considerable change—earmarked by a changing global market and competition from other European wine regions such as Italy and Spain as well as emerging New World wine producers such as California, Australia and South America.[1]
- ^ Robinson, pp. 281–83.