
A hockey stick graph or hockey stick curve is a graph, or curve shape, that resembles an ice hockey stick, in that it turns sharply from a nearly flat "blade" to a long "handle".
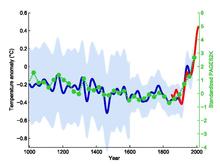
In economics,[1][2] marketing,[3] and dose–response relationships,[4][5] a hockey stick graph is one in which the "blade" is near zero (hugging the floor) before the graph turns upward to a long nearly straight increasing section. By contrast, in climate science, the well-known hockey stick graph (global temperature) describing 1000 years of global or hemispheric temperature has the "handle" horizontal and "blade" turning upward.[6] This difference of viewpoint is remarked on in a 2020 novel about climate change:
Insurance companies in a panic at last year's reports. Pay-outs at about one hundred billion USD a year now, going higher fast, as in hockey stick graph. Insurance companies insured by re-insurance. These now holding short end of stick (tall end of stick?).
— Kim Stanley Robinson, The Ministry for the Future: A Novel

- ^
Society of Plastics Engineers. Technical Conference Proceedings, Part I. Society of Plastics Engineers. 1985. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
The hockey-stick graph, which shows a magnificent turnaround in our business starting tomorrow, is familiar to all. This is partly the fault of marketing managers who, by nature, tend to be optimists; but it is also the fault of top management, who will not accept any project that promises less than spectacular results.
- ^ Taylor, John B. (1995). Economics. Houghton Mifflin. p. 33. ISBN 9780395660300. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
The long handle of the hockey stick is the sharp increase in the debt in the 1980s and 1990s. The part of the hockey stick that you hit the ball or puck with represents slower increases ...
- ^
Halfmill, Tom (July 1999). "Who Will Wire Your Home?". Maximum PC: 37. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
As usual, industry pundits are trotting out their all-purpose hockey-stick graphs to show that home networking will soon be a huge market.
- ^
Yanagimoto, Takemi; Eiji Yamamoto (1979). "Estimation of safe doses: critical review of the hockey stick regression method". Environmental Health Perspectives. 32: 193–199. doi:10.1289/ehp.7932193. PMC 1637920. PMID 540593.
The hockey stick regression method is a convenient method to estimate safe doses, which is a kind of regression method using segmented lines.
- ^ Cornfield, Jerome (18 November 1977). "Carcinogenic Risk Assessment". Science. 198 (4318): 693–699. Bibcode:1977Sci...198..693C. doi:10.1126/science.910152. PMID 910152. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
A simplified model in which a toxic substance is activated and deactivated in separate and simultaneous reactions is presented and the dose response curve implied by the model is deduced. This curve has the general form of a hockey stick, with the striking part flat or nearly flat until the dose administered saturates the deactivation system, after which the probability of a response rises rapidly.
- ^
Kerr, Richard A (2006). "Yes, it's been getting warmer in here since the CO2 began to rise". Science. 312 (5782): 1854. doi:10.1126/science.312.5782.1854. PMID 16809492. S2CID 8266929.
The resulting temperature curve sloped gently downward for most of the millennium (the handle of the hockey stick), then rose sharply into the 20th century (the blade) ...