| Hominidae[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| The eight extant hominid species, one row per genus (humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Parvorder: | Catarrhini |
| Superfamily: | Hominoidea |
| Family: | Hominidae Gray, 1825[2] |
| Type genus | |
| Homo Linnaeus, 1758
| |
| Subfamilies | |
|
sister: Hylobatidae | |
| |
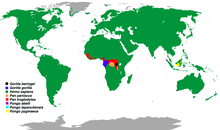
| Distribution of great ape species | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The Hominidae (/hɒˈmɪnɪdiː/), whose members are known as the great apes[note 1] or hominids (/ˈhɒmɪnɪdz/), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: Pongo (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); Gorilla (the eastern and western gorilla); Pan (the chimpanzee and the bonobo); and Homo, of which only modern humans (Homo sapiens) remain.[1]
Numerous revisions in classifying the great apes have caused the use of the term hominid to change over time. The original meaning of "hominid" referred only to humans (Homo) and their closest extinct relatives. However, by the 1990s humans and other apes were considered to be "hominids".
The earlier restrictive meaning has now been largely assumed by the term hominin, which comprises all members of the human clade after the split from the chimpanzees (Pan). The current meaning of "hominid" includes all the great apes including humans. Usage still varies, however, and some scientists and laypersons still use "hominid" in the original restrictive sense; the scholarly literature generally shows the traditional usage until the turn of the 21st century.[5]
Within the taxon Hominidae, a number of extant and extinct genera are grouped with the humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas in the subfamily Homininae; others with orangutans in the subfamily Ponginae (see classification graphic below). The most recent common ancestor of all Hominidae lived roughly 14 million years ago,[6] when the ancestors of the orangutans speciated from the ancestral line of the other three genera.[7] Those ancestors of the family Hominidae had already speciated from the family Hylobatidae (the gibbons), perhaps 15 to 20 million years ago.[7][8]
Due to the close genetic relationship between humans and the other great apes, certain animal rights organizations, such as the Great Ape Project, argue that nonhuman great apes are persons and should be given basic human rights. Twenty-nine countries have instituted research bans to protect great apes from any kind of scientific testing.[9]
- ^ a b Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 181–184. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Gray, J. E. (1825). "An outline of an attempt at the disposition of Mammalia into Tribes and Families, with a list of genera apparently appertaining to each Tribe". Annals of Philosophy. New Series. 10: 337–334.
- ^ Dawkins, R. (2005). The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of Life (p/b ed.). London, England: Phoenix (Orion Books). p. 114. ISBN 978-0-7538-1996-8.
- ^ Dawkins (2005), p. 126.
- ^ Morton, Mary. "Hominid vs. hominin". Earth Magazine. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ^ Andrew Hill; Steven Ward (1988). "Origin of the Hominidae: The Record of African Large Hominoid Evolution Between 14 My and 4 My". Yearbook of Physical Anthropology. 31 (59): 49–83. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330310505.
- ^ a b Dawkins R (2004) The Ancestor's Tale.
- ^ "Query: Hominidae/Hylobatidae". TimeTree. Temple University. 2015. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- ^ "International Bans | Laws | Release & Restitution for Chimpanzees". releasechimps.org. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).