| Human polyomavirus 2 | |
|---|---|
| |
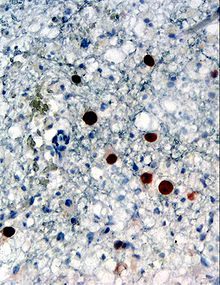
| Immunohistochemical detection of Human polyomavirus 2 protein (stained brown) in a brain biopsy (glia demonstrating progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy) | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Monodnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Shotokuvirae |
| Phylum: | Cossaviricota |
| Class: | Papovaviricetes |
| Order: | Sepolyvirales |
| Family: | Polyomaviridae |
| Genus: | Betapolyomavirus |
| Species: | Human polyomavirus 2
|
| Synonyms | |
Human polyomavirus 2, commonly referred to as the JC virus or John Cunningham virus, is a type of human polyomavirus (formerly known as papovavirus).[3] It was identified by electron microscopy in 1965 by ZuRhein and Chou,[4] and by Silverman and Rubinstein.[citation needed] It was later isolated in culture and named using the initials of a patient by the name of John Cunningham from whom it was isolated and had developed progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).[5] The virus causes leukoencephalopathy and other diseases only in cases of immunodeficiency, as in AIDS or during treatment with immunosuppressive drugs (e.g. in organ transplant patients).[6]
- ^ Calvignac-Spencer, Sébastien; et al. (22 October 2015). "Revision on the family Polyomaviridae(76 species, four genera)" (PDF). International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Retrieved 26 April 2019.
To rename the following taxon (or taxa): Current name Proposed name JC polyomavirus Human polyomavirus 2
- ^ ICTV 7th Report van Regenmortel, M.H.V., Fauquet, C.M., Bishop, D.H.L., Carstens, E.B., Estes, M.K., Lemon, S.M., Maniloff, J., Mayo, M.A., McGeoch, D.J., Pringle, C.R. and Wickner, R.B. (2000). Virus taxonomy. Seventh report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Academic Press, San Diego. p245 https://ictv.global/ictv/proposals/ICTV%207th%20Report.pdf
- ^ Rotondo JC, Candian T, Selvatici R, Mazzoni E (2017). "Tracing Males From Different Continents by Genotyping JC Polyomavirus in DNA From Semen Samples". J Cell Physiol. 232 (5): 982–985. doi:10.1002/jcp.25686. PMID 27859215. S2CID 25331955.
- ^ Zurhein, G; Chou, S. M. (1965). "Particles Resembling Papova Viruses in Human Cerebral Demyelinating Disease". Science. 148 (3676): 1477–9. Bibcode:1965Sci...148.1477R. doi:10.1126/science.148.3676.1477. PMID 14301897. S2CID 35870720.
- ^ Padgett BL, Walker DL; et al. (1971). "Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy". Lancet. 1 (7712): 1257–60. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(71)91777-6. PMID 4104715.
- ^ Ferenczy, MW; Marshall, LJ; Nelson, CD; Atwood, WJ; Nath, A; Khalili, K; Major, EO (July 2012). "Molecular biology, epidemiology, and pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, the JC virus-induced demyelinating disease of the human brain". Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 25 (3): 471–506. doi:10.1128/CMR.05031-11. PMC 3416490. PMID 22763635.