
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(6S)-3,5,6-Trihydroxy-2-(3-methylbutanoyl)-4,6-bis(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)cyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one[1] | |
| Other names
α-Lupulic acid; α-Bitter acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.371 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
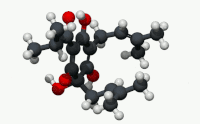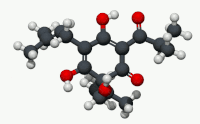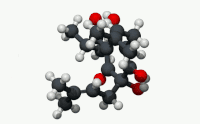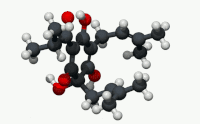
| C21H30O5 | |
| Molar mass | 362.466 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Humulone (α-lupulic acid), a vinylogous type of organic acid, is a bitter-tasting chemical compound found in the resin of mature hops (Humulus lupulus).[2] Humulone is a prevalent member of the class of compounds known as alpha acids, which collectively give hopped beer its characteristic bitter flavor.
- ^ Urban, Jan; Dahlberg, Clinton; Carroll, Brian; Kaminsky, Werner (2013). "Absolute Configuration of Beer's Bitter Compounds". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52 (5): 1553–1555. doi:10.1002/anie.201208450. PMC 3563212. PMID 23239507.
- ^ De Keukeleire, J; Ooms, G; Heyerick, A; Roldan-Ruiz, I; Van Bockstaele, E; De Keukeleire, D (2003). "Formation and accumulation of alpha-acids, beta-acids, desmethylxanthohumol, and xanthohumol during flowering of hops (Humulus lupulus L.)". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 51 (15): 4436–41. doi:10.1021/jf034263z. PMID 12848522.