| Hydrocele | |
|---|---|
| Other names | hydrocoele |
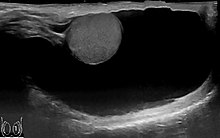 | |
| Scrotal ultrasound of a 10 cm large hydrocele, with anechoic (dark) fluid surrounding the testicle | |
| Specialty | Urology |
A hydrocele is an accumulation of serous fluid in a body cavity. A hydrocele testis, the most common form of hydrocele, is the accumulation of fluids around a testicle. It is often caused by fluid collecting within a layer wrapped around the testicle, called the tunica vaginalis, which is derived from peritoneum. Provided there is no hernia present, it goes away without treatment in the first year. Although hydroceles usually develop in males, rare instances have been described in females in the canal of Nuck.[1]
Primary hydroceles may develop in adulthood, particularly in the elderly and in hot countries, by slow accumulation of serous fluid. This is presumably caused by impaired reabsorption, which appears to be the explanation for most primary hydroceles, although the reason remains obscure.[citation needed] A hydrocele can also be the result of a plugged inguinal lymphatic system caused by repeated, chronic infection of Wuchereria bancrofti or Brugia malayi, two mosquito-borne parasites of Africa and Southeast Asia, respectively. As such, the condition would be a part of more diffuse sequelae commonly referred to as elephantiasis, which also affects the lymphatic system in other parts of the body.
- ^ Sarkar, Santanu; Panja, Soumyajyoti; Kumar, Sandeep (February 2016). "Hydrocele of the Canal of Nuck (Female Hydrocele): A Rare Differential for Inguino-Labial Swelling". Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 10 (2): PD21–PD22. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/16710.7284. ISSN 2249-782X. PMC 4800595. PMID 27042529.