 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cortef, others[1] |
| Other names | Cortisol; 11β,17α,21-Trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione; 11β,17α,21-Trihydroxyprogesterone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682206 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous, topical, rectal |
| Drug class | Glucocorticoid; Mineralocorticoid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: 96 ± 20%[11][12] |
| Protein binding | 92 ± 2% (92–93%)[11][12] |
| Metabolism | 11β-HSDs, others[12] |
| Metabolites | Cortisone, others[12] |
| Onset of action | Oral: 1.2 ± 0.4 hours (Tmax)[11] |
| Elimination half-life | 1.2–2.0 hours[11][12] |
| Duration of action | 8–12 hours[13] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
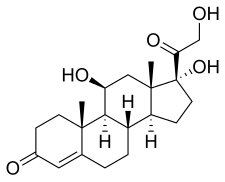
| Formula | C21H30O5 |
| Molar mass | 362.466 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication.[14] It is a corticosteroid and works as an anti-inflammatory and by immune suppression.[1] Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenital syndrome, high blood calcium, thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatitis, asthma, and COPD.[1] It is the treatment of choice for adrenocortical insufficiency.[15] It can be given by mouth, topically, or by injection.[1] Stopping treatment after long-term use should be done slowly.[1]
Side effects may include mood changes, increased risk of infection, and edema (swelling).[1] With long-term use, common side effects include osteoporosis, upset stomach, physical weakness, easy bruising, and candidiasis (yeast infections).[1] It is unclear if it is safe for use during pregnancy.[16]
Hydrocortisone was patented in 1936 and approved for medical use in 1941.[17][18] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[19] It is available as a generic medication.[1] In 2022, it was the 202nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.[20][21]
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Hydrocortisone". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 9 February 2015. Archived from the original on 20 September 2016. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
- ^ "Prescribing medicines in pregnancy database". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ "Hydrocortisone Notice of enforcement policy" (PDF). FDA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 March 2023. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ "Ala-cort- hydrocortisone cream". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 27 October 2020. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ "Ala-scalp- hydrocortisone lotion". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 21 April 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ "Alkindi Sprinkle- hydrocortisone granule". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 10 February 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ "Anusol HC- hydrocortisone acetate suppository". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 10 February 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ "Cortef- hydrocortisone tablet". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Efmody EPARwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Efmody Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. Archived from the original on 5 March 2023. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ a b c d Czock D, Keller F, Rasche FM, Häussler U (2005). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of systemically administered glucocorticoids". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 44 (1): 61–98. doi:10.2165/00003088-200544010-00003. PMID 15634032. S2CID 24458998.
- ^ a b c d e Lennernäs H, Skrtic S, Johannsson G (June 2008). "Replacement therapy of oral hydrocortisone in adrenal insufficiency: the influence of gastrointestinal factors". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 4 (6): 749–758. doi:10.1517/17425255.4.6.749. PMID 18611115. S2CID 73248541.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid23947590was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Becker KL (2001). Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 762. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2. Archived from the original on 14 September 2016.
- ^ Hamilton R (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 202. ISBN 978-1-284-05756-0.
- ^ "Hydrocortisone Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 September 2016. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ^ U.S. patent 2,183,589
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 484. ISBN 978-3-527-60749-5. Archived from the original on 10 January 2023. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Hydrocortisone Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.