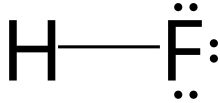
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
Fluorane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.759 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1052 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| HF | |||
| Molar mass | 20.006 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless gas or colourless liquid (below 19.5 °C) | ||
| Odor | unpleasant | ||
| Density | 1.15 g/L, gas (25 °C) 0.99 g/mL, liquid (19.5 °C) 1.663 g/mL, solid (–125 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −83.6 °C (−118.5 °F; 189.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 19.5 °C (67.1 °F; 292.6 K) | ||
| miscible (liquid) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 783 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.17 (in water),
15 (in DMSO) [2] | ||
| Conjugate acid | Fluoronium | ||
| Conjugate base | Fluoride | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.00001 | ||
| Structure | |||
| Linear | |||
| 1.86 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
8.687 J/g K (gas) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−13.66 kJ/g (gas) −14.99 kJ/g (liquid) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Highly toxic, corrosive, irritant | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H300+H310+H330, H314 | |||
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P302+P350, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | none | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
17 ppm (rat, oral) | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
1276 ppm (rat, 1 hr) 1774 ppm (monkey, 1 hr) 4327 ppm (guinea pig, 15 min)[3] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
313 ppm (rabbit, 7 hr)[3] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 3 ppm[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 3 ppm (2.5 mg/m3) C 6 ppm (5 mg/m3) [15-minute][1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
30 ppm[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Hydrogen chloride Hydrogen bromide Hydrogen iodide Hydrogen astatide | ||
Other cations
|
Sodium fluoride Potassium fluoride Rubidium fluoride Caesium fluoride | ||
Related compounds
|
Water Ammonia | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula HF. It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils at near room temperature, which is much higher of a temperature than other hydrogen halides.
Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0334". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Evans, D. A. "pKa's of Inorganic and Oxo-Acids" (PDF). Retrieved June 19, 2020.
- ^ a b "Hydrogen fluoride". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).


