| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.362 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
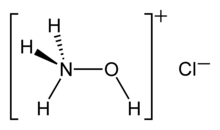
| ClH4NO | |
| Molar mass | 69.49 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.67 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 155 to 157 °C (311 to 315 °F; 428 to 430 K) decomposes |
| Conjugate base | Hydroxylamine |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    
| |
| Danger | |
| H290, H301, H302, H312, H315, H317, H319, H351, H373, H400 | |
| P201, P202, P234, P260, P261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P301+P312, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P333+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P390, P391, P404, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
|
Other cations
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hydroxylammonium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula [NH3OH]+Cl−. It is the hydrochloric acid salt of hydroxylamine (NH2OH). Hydroxylamine is a biological intermediate in nitrification (biological oxidation of ammonia with oxygen into nitrite) and in anammox (biological oxidation of nitrite and ammonium into dinitrogen gas) which are important in the nitrogen cycle in soil and in wastewater treatment plants.
