 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Anaspaz, Levbid, Levsin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a684010 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, Injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% protein binding |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 3–5 hrs. |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.667 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
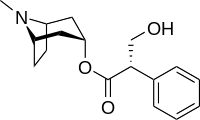
| Formula | C17H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 289.375 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Hyoscyamine (also known as daturine or duboisine) is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid and plant toxin. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the family Solanaceae, including henbane, mandrake, angel's trumpets, jimsonweed, the sorcerers' tree, and Atropa belladonna (deadly nightshade). It is the levorotary isomer of atropine (third of the three major nightshade alkaloids) and thus sometimes known as levo-atropine.[1]
In 2021, it was the 272nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 900,000 prescriptions.[2][3]
- ^ Ushimaru R, Ruszczycky MW, Liu HW (January 2019). "Changes in Regioselectivity of H Atom Abstraction during the Hydroxylation and Cyclization Reactions Catalyzed by Hyoscyamine 6β-Hydroxylase". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 141 (2): 1062–1066. doi:10.1021/jacs.8b11585. PMC 6488026. PMID 30545219.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Hyoscyamine - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 14 January 2024.