| Hyperalgesia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
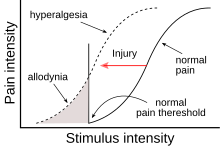
Hyperalgesia (/ˌhaɪpərælˈdʒiːziə/ or /-siə/; hyper from Greek ὑπέρ (huper) 'over' + -algesia from Greek ἄλγος (algos) 'pain') is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and can cause hypersensitivity to stimulus. Prostaglandins E and F are largely responsible for sensitizing the nociceptors.[1] Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of sickness behavior, the evolved response to infection.[2]
- ^ "Clinical Pharmacology". www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com. Archived from the original on 2019-12-10. Retrieved 2017-06-25.
- ^ Hart BL (1988). "Biological basis of the behavior of sick animals". Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 12 (2): 123–37. doi:10.1016/S0149-7634(88)80004-6. PMID 3050629. S2CID 17797005.