This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2023) |
| Geometry |
|---|
 |
| Geometers |

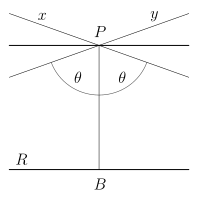
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or Bolyai–Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with:
- For any given line R and point P not on R, in the plane containing both line R and point P there are at least two distinct lines through P that do not intersect R.
(Compare the above with Playfair's axiom, the modern version of Euclid's parallel postulate.)
The hyperbolic plane is a plane where every point is a saddle point. Hyperbolic plane geometry is also the geometry of pseudospherical surfaces, surfaces with a constant negative Gaussian curvature. Saddle surfaces have negative Gaussian curvature in at least some regions, where they locally resemble the hyperbolic plane.
The hyperboloid model of hyperbolic geometry provides a representation of events one temporal unit into the future in Minkowski space, the basis of special relativity. Each of these events corresponds to a rapidity in some direction.
When geometers first realised they were working with something other than the standard Euclidean geometry, they described their geometry under many different names; Felix Klein finally gave the subject the name hyperbolic geometry to include it in the now rarely used sequence elliptic geometry (spherical geometry), parabolic geometry (Euclidean geometry), and hyperbolic geometry. In the former Soviet Union, it is commonly called Lobachevskian geometry, named after one of its discoverers, the Russian geometer Nikolai Lobachevsky.