| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hypodiphosphoric acid
| |
| Other names
Diphosphoric acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
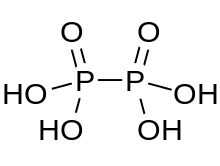
| H4P2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 161.98 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid (dihydrate) |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.2, 2.8, 7.3, 10.0[1] |
| Conjugate base | Hypophosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hypophosphoric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H4P2O6, with phosphorus in a formal oxidation state of +4. In the solid state it is present as the dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O. In hypophosphoric acid the phosphorus atoms are identical and joined directly with a P−P bond. Isohypophosphoric acid is a structural isomer of hypophosphoric acid in which one phosphorus has a hydrogen directedly bonded to it and that phosphorus atom is linked to the other one by an oxygen bridge to give a phosphorous acid/phosphoric acid mixed anhydride. The two phosphorus atoms are in the +3 and +5 oxidation states, respectively.