This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
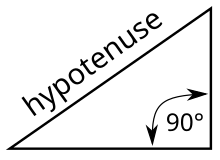
In geometry, a hypotenuse is the side of a right triangle opposite the right angle.[1] It is the longest side of any such triangle; the two other shorter sides of such a triangle are called catheti or legs. The length of the hypotenuse can be found using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two legs. Mathematically, this can be written as , where a is the length of one leg, b is the length of another leg, and c is the length of the hypotenuse.[2]
For example, if one of the legs of a right angle has a length of 3 and the other has a length of 4, then their squares add up to 25 = 9 + 16 = 3 × 3 + 4 × 4. Since 25 is the square of the hypotenuse, the length of the hypotenuse is the square root of 25, that is, 5. In other words, if and , then .
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 27 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 258.
...Also a right-angled triangle has one angle a right angle, the side opposite this angle being called the hypotenuse;...
- ^ Jr, Jesse Moland (August 2009). I Hate Trig!: A Practical Guide to Understanding Trigonometry. Jesse Moland. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-4486-4707-1.



