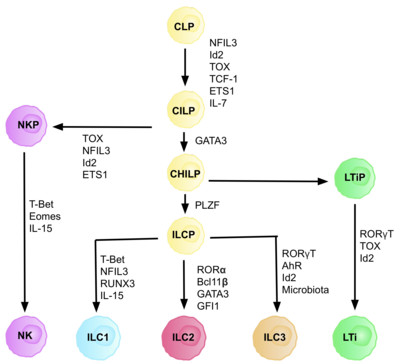
ILC2 cells, or type 2 innate lymphoid cells are a type of innate lymphoid cell. Not to be confused with the ILC. They are derived from common lymphoid progenitor and belong to the lymphoid lineage. These cells lack antigen specific B or T cell receptor because of the lack of recombination activating gene.[2] ILC2s produce type 2 cytokines (e.g. IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13) and are involved in responses to helminths, allergens,[3] some viruses, such as influenza virus[4] and cancer.[5][6][7]
The cell type was first described in 2001 as non-B/non-T cells, which produced IL-5 and IL-13 in response to IL-25 and expressed MHC class II and CD11c.[8] In 2006, a similar cell population was identified in a case of helminthic infection.[9] The name "ILC2" was not proposed until 2013.[10] They were previously identified in literature as natural helper cells,[11] nuocytes,[12] or innate helper 2 cells.[13] It is believed that ILC2s are rather old cell type with ancestor populations emerging in lamprey and bony fish.[14]
- ^ Vivier E, Artis D, Colonna M, Diefenbach A, Di Santo JP, Eberl G, et al. (August 2018). "Innate Lymphoid Cells: 10 Years On". Cell. 174 (5): 1054–1066. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.017. PMID 30142344.
- ^ Spits H, Cupedo T (2012). "Innate lymphoid cells: emerging insights in development, lineage relationships, and function". Annual Review of Immunology. 30: 647–75. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075053. PMID 22224763.
- ^ Doherty TA, Broide DH (January 2019). "Airway innate lymphoid cells in the induction and regulation of allergy". Allergology International. 68 (1): 9–16. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2018.11.001. PMC 6614863. PMID 30473412.
- ^ Monticelli LA, Sonnenberg GF, Abt MC, Alenghat T, Ziegler CG, Doering TA, et al. (November 2011). "Innate lymphoid cells promote lung-tissue homeostasis after infection with influenza virus". Nature Immunology. 12 (11): 1045–54. doi:10.1038/ni.2131. PMC 3320042. PMID 21946417.
- ^ Wagner, Marek; Ealey, Kafi N.; Tetsu, Hiroe; Kiniwa, Tsuyoshi; Motomura, Yasutaka; Moro, Kazuyo; Koyasu, Shigeo (February 2020). "Tumor-Derived Lactic Acid Contributes to the Paucity of Intratumoral ILC2s". Cell Reports. 30 (8): 2743–2757.e5. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.103. hdl:11250/2763785. PMID 32101749.
- ^ Wagner, Marek; Koyasu, Shigeo (May 2019). "Cancer Immunoediting by Innate Lymphoid Cells". Trends in Immunology. 40 (5): 415–430. doi:10.1016/j.it.2019.03.004. PMID 30992189. S2CID 119093972.
- ^ Wagner, Marek; Moro, Kazuyo; Koyasu, Shigeo (May 2017). "Plastic Heterogeneity of Innate Lymphoid Cells in Cancer". Trends in Cancer. 3 (5): 326–335. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2017.03.008. PMID 28718410.
- ^ Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, Li J, Zurawski SM, Lo S, et al. (December 2001). "IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo". Immunity. 15 (6): 985–95. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(01)00243-6. PMID 11754819.
- ^ Fallon PG, Ballantyne SJ, Mangan NE, Barlow JL, Dasvarma A, Hewett DR, et al. (April 2006). "Identification of an interleukin (IL)-25-dependent cell population that provides IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 at the onset of helminth expulsion". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 203 (4): 1105–16. doi:10.1084/jem.20051615. PMC 2118283. PMID 16606668.
- ^ Lund S, Walford HH, Doherty TA (November 2013). "Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergic Disease". Current Immunology Reviews. 9 (4): 214–221. doi:10.2174/1573395510666140304235916. PMC 4033554. PMID 24876829.
- ^ Moro K, Yamada T, Tanabe M, Takeuchi T, Ikawa T, Kawamoto H, et al. (January 2010). "Innate production of T(H)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(+)Sca-1(+) lymphoid cells". Nature. 463 (7280): 540–4. doi:10.1038/nature08636. PMID 20023630. S2CID 4420895.
- ^ Neill DR, Wong SH, Bellosi A, Flynn RJ, Daly M, Langford TK, et al. (April 2010). "Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity". Nature. 464 (7293): 1367–70. Bibcode:2010Natur.464.1367N. doi:10.1038/nature08900. PMC 2862165. PMID 20200518.
- ^ Price AE, Liang HE, Sullivan BM, Reinhardt RL, Eisley CJ, Erle DJ, et al. (June 2010). "Systemically dispersed innate IL-13-expressing cells in type 2 immunity". Proc Natl Acad Sci. 107 (25): 11489–94. doi:10.1073/pnas.1003988107. PMC 2895098. PMID 20534524.
- ^ Vivier, Eric; van de Pavert, Serge A; Cooper, Max D; Belz, Gabrielle T (2016-06-21). "The evolution of innate lymphoid cells". Nature Immunology. 17 (7): 790–794. doi:10.1038/ni.3459. ISSN 1529-2908. PMC 5287353. PMID 27328009.