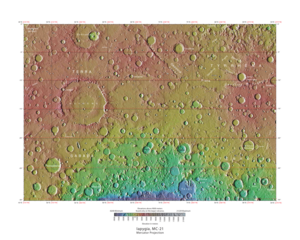
 Map of Iapygia quadrangle from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. The highest elevations are red and the lowest are blue. Terby (crater) contains many rock layers. | |
| Coordinates | 15°00′S 292°30′W / 15°S 292.5°W |
|---|---|

The Iapygia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Iapygia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-21 (Mars Chart-21).[1] It was named after the heel of the boot of Italy. That name was given by the Greeks[2] It is part of a region of Italy named Apulia.[3][circular reference] The name Iapygia was approved in 1958.[4]
The Iapygia quadrangle covers the area from 270° to 315° west longitude and from 0° to 30° south latitude on Mars. Parts of the regions Tyrrhena Terra and Terra Sabaea are found in this quadrangle. The largest crater in this quadrangle is Huygens. Some interesting features in this quadrangle are dikes.[5] the many layers found in Terby crater, and the presence of carbonates on the rim of Huygens crater.[6]
- ^ Davies, M.E.; Batson, R.M.; Wu, S.S.C. “Geodesy and Cartography” in Kieffer, H.H.; Jakosky, B.M.; Snyder, C.W.; Matthews, M.S., Eds. Mars. University of Arizona Press: Tucson, 1992.
- ^ "Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), IABA´DIUS, IABA´DIUS, IAPY´GIA".
- ^ Apulia
- ^ "Planetary Names". planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov.
- ^ Head, J. et al. 2006. The Huygens-Hellas giant dike system on Mars: Implications for Late Noachian-Early Hesperian volcanic resurfacing and climatic evolution. Geology. 34:4: 285-288.
- ^ "Some of Mars' Missing Carbon Dioxide May be Buried". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Archived from the original on 2011-06-29. Retrieved 2011-03-10.