| Ileum | |
|---|---|
 Small intestine | |
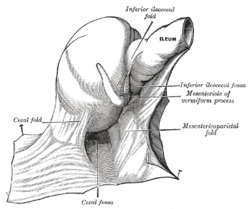 The cecal fossa. The ileum and cecum are drawn backward and upward. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Midgut |
| Artery | Ileal arteries, ileocolic artery |
| Vein | Ileal veins |
| Nerve | Celiac ganglia, vagus[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ileum |
| MeSH | D007082 |
| TA98 | A05.6.04.001 |
| TA2 | 2959 |
| FMA | 7208 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
 |
| Major parts of the |
| Gastrointestinal tract |
|---|
The ileum (/ˈɪliəm/) is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum.[2] Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum.
The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV). In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and the pH is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly basic).
Ileum is derived from the Greek word εἰλεός (eileós), referring to a medical condition known as ileus.[citation needed]
- ^ Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 6/6ch2/s6ch2_30". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24.
- ^ Guillaume, Jean; Praxis Publishing; Sadasivam Kaushik; Pierre Bergot; Robert Metailler (2001). Nutrition and Feeding of Fish and Crustaceans. Springer. p. 31. ISBN 1-85233-241-7. Retrieved 2009-01-09.