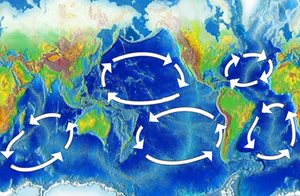
The Indian Ocean garbage patch, discovered in 2010, is a marine garbage patch, a gyre of marine litter, suspended in the upper water column of the central Indian Ocean, specifically the Indian Ocean Gyre, one of the five major oceanic gyres.[1][2][3][4][5][6] The patch does not appear as a continuous debris field. As with other patches in each of the five oceanic gyres, the plastics in it break down to ever smaller particles, and to constituent polymers.[7] As with the other patches, the field constitutes an elevated level of pelagic plastics, chemical sludge, and other debris; primarily particles that are invisible to the naked eye. The concentration of particle debris has been estimated to be approximately 10,000 particles per square kilometer.[8][9][10][11]
- ^ "Ocean Geography ~ MarineBio Conservation Society". www.marinebio.org. 17 June 2018. Retrieved 17 September 2021.
- ^ First Voyage to South Atlantic Pollution Site SustainableBusiness.com News access-date=10 December 2021
- ^ New garbage patch discovered in Indian Ocean Archived 2 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Lori Bongiorno, Green Yahoo, 27 July 2010
- ^ Opinion: Islands are 'natural nets' for plastic-choked seas Archived 6 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine Marcus Eriksen for CNN, Petroleum, CNN Tech 24 June 2010
- ^ Our Ocean Backyard: Exploring plastic seas Archived 20 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine, Dan Haifley, 15 May 2010, Santa Cruz Sentinel
- ^ Life aquatic choked by plastic Archived 14 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine 14 November 2010, Times Live
- ^ Moore, Charles (November 2003). "Across the Pacific Ocean, plastics, plastics, everywhere". Natural History Magazine. Archived from the original on 6 July 2009.
- ^ Sesini, Marzia (August 2011). "The Garbage Patch In The Oceans: The Problem And Possible Solutions" (PDF). Columbia University.
- ^ For a discussion of the current sampling techniques and particle size, see Peter Ryan, Charles Moore et al., Monitoring the abundance of plastic debris in the marine environment. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 27 July 2009 vol. 364 no. 1526 1999–2012, doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0207
- ^ "OSU: Reports of giant ocean 'garbage patch' are exaggerated". 4 January 2011. Archived from the original on 14 February 2011. Retrieved 7 January 2011.
- ^ Transoceanic Trash: International and United States Strategies for the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, Susan L. Dautel, 3 Golden Gate U. Envtl. L.J. 181 (2009)