This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (December 2015) |  |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
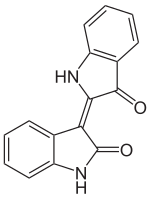
| IUPAC name
(3Z)-3-(3-Oxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-ylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
| |
| Other names
Indigo red
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.119.646 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H10N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 262.268 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Indirubin is a chemical compound most often produced as a byproduct of bacterial metabolism. For instance, it is one of the compounds responsible for the generally benign condition purple urine bag syndrome, resulting from bacteria metabolizing indoxyl sulfate found naturally in urine.
Indirubin is a structural isomer (more precisely is position isomer) of indigo dye.