This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2019) |
| Indo-Iranian | |
|---|---|
| Indo-Iranic (Aryan) | |
| Geographic distribution | South, Central, West Asia and the Caucasus |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Indo-Iranian |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-5 | iir |
| Glottolog | indo1320 |
 Distribution of the Indo-Iranian languages | |
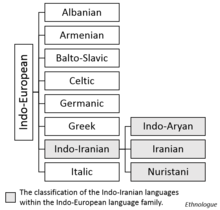
The Indo-Iranian languages (also known as Indo-Iranic languages[2][3] or collectively the Aryan languages[4]) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.5 billion speakers, predominantly in South Asia, West Asia and parts of Central Asia.
The areas with Indo-Iranian languages stretch from Europe (Romani) and the Caucasus (Ossetian, Tat and Talysh), down to Mesopotamia and eastern Anatolia (Kurdish languages, Gorani, Kurmanji Dialect continuum,[5] Zaza[6][7]), the Levant (Domari)[8] and Iran (Persian), eastward to Xinjiang (Sarikoli) and Assam (Assamese), and south to Sri Lanka (Sinhala) and the Maldives (Maldivian), with branches stretching as far out as Oceania and the Caribbean for Fiji Hindi and Caribbean Hindustani respectively. Furthermore, there are large diaspora communities of Indo-Iranian speakers in northwestern Europe (the United Kingdom), North America (United States, Canada), Australia, South Africa, and the Persian Gulf Region (United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia). The number of distinct languages listed in Ethnologue are 312,[9] while those recognised in Glottolog are 320.[10] The Indo-Iranian language with the largest number of native speakers is the Hindustani language (Hindi-Urdu).[11]
- ^ Bashir, Elena (2007). "Dardic". In Jain, Danesh; Cardona, George (eds.). The Indo-Aryan languages. Routledge. p. 905. ISBN 978-0-415-77294-5.
'Dardic' is a geographic cover term for those Northwest Indo-Aryan languages which [...] developed new characteristics different from the IA languages of the Indo-Gangetic plain. Although the Dardic and Nuristani (previously 'Kafiri') languages were formerly grouped together, Morgenstierne (1965) has established that the Dardic languages are Indo-Aryan, and that the Nuristani languages constitute a separate subgroup of Indo-Iranian.
- ^ Mahulkar, D. D. (1990). Pre-Pāṇinian Linguistic Studies. Northern Book Centre. ISBN 978-81-85119-88-5.
- ^ Puglielli, Annarita; Frascarelli, Mara (2011). Linguistic Analysis: From Data to Theory. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-022250-0.
- ^ Gvozdanović, Jadranka (1999). Numeral Types and Changes Worldwide. Walter de Gruyter. p. 221. ISBN 978-3-11-016113-7.
The usage of 'Aryan languages' is not to be equated with Indo-Aryan languages, rather Indo-Iranic languages of which Indo-Aryan is a subgrouping.
- ^ Chatoev, Vladimir; Kʻosyan, Aram (1999). Nationalities of Armenia. YEGEA Publishing House. p. 61. ISBN 978-99930-808-0-0.
- ^ Asatrian, Garnik (1995). "DIMLĪ". Encyclopedia Iranica. VI. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- ^ Paul, Ludwig (1998). "The Pozition of Zazaki the West Iranian Languages" (PDF). Iran Chamber. Open Publishing. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ^ Matras 2012.
- ^ "Indo-Iranian". Ethnologue. 2023.
- ^ "Glottolog 4.7 – Indo-Iranian". Glottolog. Retrieved 1 February 2023.
- ^ "Hindi" L1: 322 million (2011 Indian census), including perhaps 150 million speakers of other languages that reported their language as "Hindi" on the census. L2: 274 million (2016, source unknown). Urdu L1: 67 million (2011 & 2017 censuses), L2: 102 million (1999 Pakistan, source unknown, and 2001 Indian census): Ethnologue 21. Hindi at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018)
 . Urdu at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018)
. Urdu at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018)  .
.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).