 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ɪndoʊˈmɛtəsɪn/ |
| Trade names | Indocid, Indocin |
| Other names | Indomethacin (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, rectal, intravenous, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100% (oral), 80–90% (rectal) |
| Protein binding | 99%[2] |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 2.6-11.2 hours (adults), 12-28 hours (infants)[2] |
| Excretion | Kidney (60%), fecal (33%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.170 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
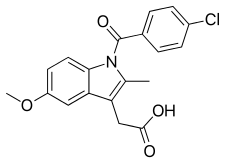
| Formula | C19H16ClNO4 |
| Molar mass | 357.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Indometacin, also known as indomethacin, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used as a prescription medication to reduce fever, pain, stiffness, and swelling from inflammation. It works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, endogenous signaling molecules known to cause these symptoms. It does this by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme that catalyzes the production of prostaglandins.[2][3]
It was patented in 1961 and approved for medical use in 1963.[4][5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] In 2021, it was the 253rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.[7][8]
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ a b c Brayfield A, ed. (14 January 2014). "Indometacin". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ^ "TGA Approved Terminology for Medicines, Section 1 – Chemical Substances" (PDF). Therapeutic Goods Administration, Department of Health and Ageing, Australian Government. July 1999. p. 70.
- ^ Hart FD, Boardman PL (October 1963). "Indomethacin: A New Non-steroid Anti-inflammatory Agent". British Medical Journal. 2 (5363): 965–970. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5363.965. PMC 1873102. PMID 14056924.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 517. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Indomethacin - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 14 January 2024.