This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2020) |
| Infectious bursal disease virus | |
|---|---|
| |
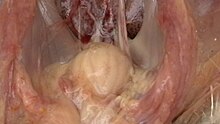
| Enlarged bursa of Fabricius with yellowish peribursal oedema | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | incertae sedis |
| Family: | Birnaviridae |
| Genus: | Avibirnavirus |
| Species: | Infectious bursal disease virus
|
Infectious bursal disease (IBD), also known as Gumboro disease, infectious bursitis, and infectious avian nephrosis, is a highly contagious disease of young chickens and turkeys caused by infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV),[1] characterized by immunosuppression and mortality generally at 3 to 6 weeks of age. The disease was first discovered in Gumboro, Delaware in 1962. It is economically important to the poultry industry worldwide due to increased susceptibility to other diseases and negative interference with effective vaccination. In recent years, very virulent strains of IBDV (vvIBDV), causing severe mortality in chicken, have emerged in Europe, Latin America, South-East Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Infection is via the oro-fecal route, with affected birds excreting high levels of the virus for approximately 2 weeks after infection. The disease is easily spread from infected chickens to healthy chickens through food, water, and physical contact.[2]
- ^ Castón, José R.; Rodríguez, José F.; Carrascosa, José L. (2008). "Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV)". Segmented Double-stranded RNA Viruses: Structure and Molecular Biology. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-21-9.
- ^ Nguyen Thi Hau (October 27, 2014). "GUMBORO disease in chickens and methods of prevention and treatment"