| Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |
|---|---|
 Muscles of the pharynx and cheek. (Constrictor pharyngis inferior visible at bottom left.) | |
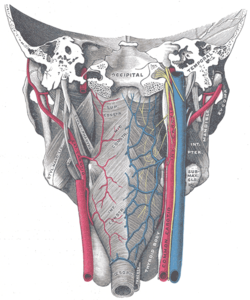 Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves. (Inf. const. labeled at bottom center.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Cricoid cartilage and thyroid cartilage |
| Insertion | Pharyngeal raphe |
| Nerve | Pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve, recurrent laryngeal nerve and superior laryngeal nerve |
| Actions | Swallowing |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus constrictor pharyngis inferior |
| TA98 | A05.3.01.111 |
| TA2 | 2187 |
| FMA | 46623 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a skeletal muscle of the neck. It is the thickest of the three outer pharyngeal muscles. It arises from the sides of the cricoid cartilage and the thyroid cartilage. It is supplied by the vagus nerve (CN X). It is active during swallowing, and partially during breathing and speech. It may be affected by Zenker's diverticulum.