Infragravity waves are surface gravity waves with frequencies lower than the wind waves – consisting of both wind sea and swell – thus corresponding with the part of the wave spectrum lower than the frequencies directly generated by forcing through the wind.
Infragravity waves are ocean surface gravity waves generated by ocean waves of shorter periods. The amplitude of infragravity waves is most relevant in shallow water, in particular along coastlines hit by high amplitude and long period wind waves and ocean swells. Wind waves and ocean swells are shorter, with typical dominant periods of 1 to 25 s. In contrast, the dominant period of infragravity waves is typically 80 to 300 s,[1] which is close to the typical periods of tsunamis, with which they share similar propagation properties including very fast celerities in deep water. This distinguishes infragravity waves from normal oceanic gravity waves, which are created by wind acting on the surface of the sea, and are slower than the generating wind.
Whatever the details of their generation mechanism, discussed below, infragravity waves are these subharmonics of the impinging gravity waves.[2]
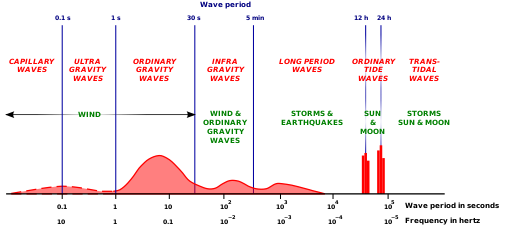
Technically infragravity waves are simply a subcategory of gravity waves and refer to all gravity waves with periods greater than 30 s. This could include phenomena such as tides and oceanic Rossby waves, but the common scientific usage is limited to gravity waves that are generated by groups of wind waves.
The term "infragravity wave" appears to have been coined by Walter Munk in 1950.[3][4]
- ^ Ardhuin, Fabrice; Arshad Rawat; Jerome Aucan (2014), "A numerical model for free infragravity waves: Definition and validation at regional and global scales", Ocean Modelling, vol. 77, Elsevier, pp. 20–32
- ^ Bromirski, Peter D.; Olga V. Sergienko; Douglas R. MacAyeal (2010). "Transoceanic infragravity waves impacting Antarctic ice shelves". Geophysical Research Letters. 37 (L02502): n/a. Bibcode:2010GeoRL..37.2502B. doi:10.1029/2009GL041488. S2CID 38071443.
- ^ a b Munk, Walter H. (1950), "Origin and generation of waves", Proceedings 1st International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Long Beach, California: ASCE, pp. 1–4, doi:10.9753/icce.v1.1, ISSN 2156-1028
- ^ Kinsman, Blair (1965). Wind Waves: Their Generation and Propagation on the Ocean Surface. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. pp. 22–23. OCLC 489729.