| Infraorbital foramen | |
|---|---|
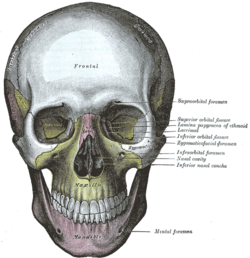 The skull from the front. (Infraorbital foramen labeled at center right, under the eye.) | |
 Articulation of nasal and lacrimal bones with maxilla. (Infraorbital foramen labeled at left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen infraorbitale |
| TA98 | A02.1.12.008 |
| TA2 | 763 |
| FMA | 57718 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is one of two small holes in the skull's upper jawbone (maxillary bone), located below the eye socket and to the left and right of the nose. Both holes are used for blood vessels and nerves. In anatomical terms, it is located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve. It is typically 6.10 to 10.9 mm (0.240 to 0.429 in) from the infraorbital margin.[1]
- ^ Macedo, VC; Cabrini, RR; Faig-Leite, H (2009). "Infraorbital foramen location in dry human skulls" (PDF). Braz. J. Morphol. Sci. 26 (1): 35–38. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2011-12-03.