This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2015) |
| Interventricular septum | |
|---|---|
 Section of the heart showing the ventricular septum. | |
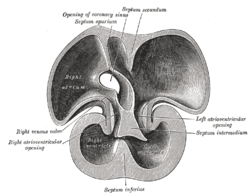 Interior dorsal half of heart of nearly 5 weeks old human embryo. (Labeled as 'septum inferius') | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Heart |
| Artery | anterior interventricular branch of left coronary artery and Posterior interventricular artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | septum interventriculare cordis |
| MeSH | D054088 |
| TA98 | A12.1.00.013 |
| TA2 | 3970 |
| FMA | 7133 |
| Anatomical terminology | |

The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The interventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior interventricular sulci. The lower part of the septum, which is the major part, is thick and muscular, and its much smaller upper part is thin and membraneous.[1]
During each cardiac cycle the interventricular septum contracts by shortening longitudinally and becoming thicker.