| Intracranial hemorrhage | |
|---|---|
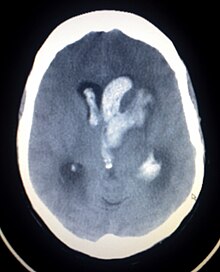 | |
| Axiali CT scan of a spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine |
| Symptoms | Same symptoms as ischemic stroke, but unconsciousness, headache, nausea, stiff neck, and seizures are more often in brain hemorrhages than ischemic strokes |
| Complications | Coma, persistent vegetative state, cardiac arrest (when bleeding is in the brain stem or is severe), death |
| Types | Intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, epidural bleed, subdural bleed |
| Causes | Stroke, head injury, ruptured aneurysm |
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), also known as intracranial bleed, is bleeding within the skull.[1] Subtypes are intracerebral bleeds (intraventricular bleeds and intraparenchymal bleeds), subarachnoid bleeds, epidural bleeds, and subdural bleeds.[2]
Intracerebral bleeding affects 2.5 per 10,000 people each year.[1]
- ^ a b Caceres JA, Goldstein JN (August 2012). "Intracranial hemorrhage". Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 30 (3): 771–794. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2012.06.003. PMC 3443867. PMID 22974648.
- ^ Naidich TP, Castillo M, Cha S, Smirniotopoulos JG (2012). Imaging of the Brain, Expert Radiology Series,1: Imaging of the Brain. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 387. ISBN 978-1416050094.