| Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm | |
|---|---|
| Other names | IPMN |
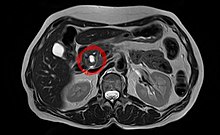 | |
| Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in magnetic resonance imaging. | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Symptoms | Usually asymptomatic |
| Usual onset | 50-70 years of age |
| Types | Main duct, branch duct or mixed |
| Risk factors | Male gender |
| Differential diagnosis | Mucinous cystic neoplasm |
| Treatment | Imaging surveillance, surgical resection |
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a type of tumor that can occur within the cells of the pancreatic duct. IPMN tumors produce mucus,[1] and this mucus can form pancreatic cysts.[2] Although intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms are benign tumors, they can progress to pancreatic cancer.[1] As such IPMN is viewed as a precancerous condition.[3] Once an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm has been found, the management options include close monitoring and pre-emptive surgery.[medical citation needed]
- ^ a b "Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas". Johns Hopkins University. Archived from the original on 4 February 2021. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ Campbell, NM; Katz, SS; Escalon, JG; Do, RK (March 2015). "Imaging patterns of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an illustrated discussion of the International Consensus Guidelines for the Management of IPMN". Abdominal Imaging. 40 (3): 663–77. doi:10.1007/s00261-014-0236-4. PMID 25219664. S2CID 10097983.
- ^ "Precancerous conditions of the pancreas - Canadian Cancer Society". www.cancer.ca. Retrieved 5 November 2017.