 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Camptosar, Campto, Onivyde, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608043 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | NA |
| Metabolism | Liver glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 6 to 12 hours |
| Excretion | Bile duct and kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.219.260 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
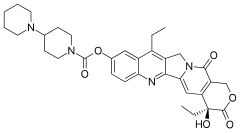
| Formula | C33H38N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 586.689 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Irinotecan, sold under the brand name Camptosar among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat colon cancer and small cell lung cancer.[8] For colon cancer it is used either alone or with fluorouracil.[8] For small cell lung cancer it is used with cisplatin.[8] It is given intravenously.[8]
Common side effects include diarrhea, vomiting, bone marrow suppression, hair loss, shortness of breath, and fever.[8] Other severe side effects include blood clots, colon inflammation, and allergic reactions.[8] Those with two copies of the UGT1A1*28 gene variant are at higher risk for side effects.[8] Use during pregnancy can result in harm to the baby.[8] Irinotecan is a topoisomerase inhibitor[9]—it blocks the topoisomerase I enzyme, resulting in DNA damage and cell death.[8]
Irinotecan was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996.[8] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[10] It is made from the natural compound camptothecin which is found in the Chinese ornamental tree Camptotheca acuminata.[8][11]
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2016". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ "Product monograph brand safety updates". Health Canada. 7 July 2016. Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- ^ "Cancer therapies". Health Canada. 8 May 2018. Retrieved 13 April 2024.
- ^ "Onivyde pegylated liposomal 4.3 mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 18 February 2020. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Camptosar FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Onivyde FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Onivyde EPARwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Irinotecan Hydrochloride". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. p. 624. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ Heinrich M, Barnes J, Gibbons S, Williamson EM (2012). Fundamentals of pharmacognosy and phytotherapy (2nd ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. p. 130. ISBN 978-0-7020-5231-6. OCLC 802051297.